Sunflower Seed Viability
Can you plant sunflower seeds from a sunflower – Successfully growing sunflowers from seeds harvested from your own plants depends largely on the viability of those seeds. Several factors influence how well your seeds will germinate and grow into healthy plants. Understanding these factors and employing proper seed handling techniques is crucial for a successful harvest.
Factors Affecting Sunflower Seed Viability
Several factors contribute to the viability of sunflower seeds. Seed maturity at harvest is paramount; seeds harvested too early may not be fully developed and lack the necessary resources for germination. Conversely, seeds left on the plant too long might become damaged by pests, diseases, or harsh weather conditions, reducing their viability. Proper drying and storage techniques are also vital in maintaining seed viability.
High humidity and improper storage can lead to mold growth and seed degradation.
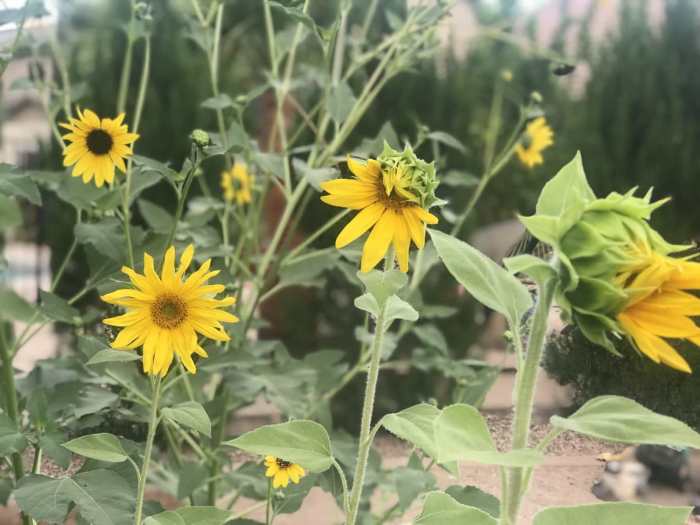
Determining Seed Viability: A Simple Home Test

Source: lsdaynursery.com
A simple test can help assess seed viability before planting. Select a representative sample of seeds and place them between two moist paper towels in a sealed plastic bag. Keep the bag in a warm location (around 70-75°F or 21-24°C). After a few days, check for germination. The percentage of seeds that germinate provides an estimate of viability.
A high germination rate indicates good seed quality.
Germination Rates Across the Sunflower Head
Seeds from different parts of the sunflower head may exhibit varying germination rates. Seeds in the center of the head often mature earlier and may have slightly higher germination rates compared to those on the outer edges. This difference is likely due to variations in nutrient availability and exposure to sunlight during development.
Proper Storage of Sunflower Seeds
Proper storage is crucial for maintaining seed viability. Seeds should be thoroughly dried to a moisture content of around 6-8% before storage. Store seeds in airtight containers in a cool, dark, and dry place. Refrigeration (around 40°F or 4°C) can further extend seed viability. Avoid storing seeds in areas with fluctuating temperatures or high humidity.
Seed Preparation and Planting: Can You Plant Sunflower Seeds From A Sunflower
Preparing the seeds and soil correctly is crucial for successful sunflower cultivation. The choice of planting method (direct sowing versus starting indoors) also impacts the final outcome. Optimal conditions are essential for healthy germination and growth.
Optimal Conditions for Planting Sunflower Seeds
Sunflowers thrive in full sun (at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily), well-drained soil, and warm temperatures (ideally above 60°F or 15°C). While they tolerate a range of soil types, loose, fertile soil rich in organic matter is preferred. Proper soil preparation ensures good drainage and aeration, promoting healthy root development.
Planting Methods: Direct Sowing vs. Starting Indoors
| Method | Pros | Cons | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Sowing | Simpler, less labor-intensive | Slower germination, higher risk of seed predation | Warmer climates, established gardens |
| Starting Indoors | Faster germination, higher success rate, protection from pests | More labor-intensive, requires transplanting | Cooler climates, shorter growing seasons |
Planting Depth and Spacing
Illustration: Imagine a cross-section of the soil. The soil is depicted as dark brown, loose, and crumbly. The seeds, approximately 1/2 inch (1.25 cm) long and oval-shaped, are a dark grey-brown color. Each seed is planted about 1 inch (2.5 cm) deep, with approximately 6-12 inches (15-30 cm) of space between seeds. The illustration shows the seed placed horizontally in the soil with the pointed end slightly upward.
Soil Preparation Before Planting
Preparing the soil involves removing weeds, rocks, and debris. Loosening the soil to a depth of at least 12 inches (30 cm) improves drainage and aeration. Incorporating organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, enhances soil fertility and provides essential nutrients for the sunflowers.
Germination and Early Growth
Once planted, the sunflower seeds will begin to germinate and develop into seedlings. Understanding the typical timeline, potential problems, and environmental factors is key to ensuring successful early growth.
Sunflower Germination and Early Seedling Development Timeline

Source: publicdomainpictures.net
Under ideal conditions, sunflower seeds typically germinate within 7-10 days. Seedlings emerge from the soil, initially developing a pair of cotyledons (seed leaves). True leaves then appear, followed by rapid stem elongation. This early growth stage is crucial for establishing a strong root system and preparing for subsequent growth.
Common Germination Problems and Solutions
Common problems include poor seed viability, insufficient moisture, and soil compaction. Addressing these issues involves using high-quality seeds, ensuring adequate watering, and preparing the soil properly. Seed rot can occur if the soil is too wet; good drainage is essential. Pests like birds or rodents may also damage seeds or seedlings.
Environmental Factors Affecting Germination, Can you plant sunflower seeds from a sunflower
Temperature, moisture, and sunlight are crucial environmental factors. Optimal temperatures for germination are between 60-80°F (15-27°C). Consistent moisture is essential, but overwatering can lead to problems. Adequate sunlight is crucial for photosynthesis and seedling development.
Tips for Successful Sunflower Seedling Care
- Ensure consistent moisture, but avoid overwatering.
- Protect seedlings from pests and diseases.
- Provide adequate sunlight.
- Thin seedlings if necessary to ensure proper spacing.
- Monitor for signs of disease or nutrient deficiencies.
Growth and Maturation

Source: ufl.edu
From seedling to mature plant, sunflowers undergo a remarkable transformation. Understanding their growth stages, nutritional needs, and signs of health is essential for successful cultivation.
Stages of Sunflower Growth
The sunflower lifecycle begins with germination, followed by the seedling stage characterized by rapid stem and leaf development. The vegetative stage sees substantial height increase and leaf production. The reproductive stage involves the development of flower buds, followed by flowering and seed formation. Finally, the maturation stage marks seed ripening and the plant’s senescence.
Growth Rate Comparison: Homegrown vs. Purchased Seeds
While there may be some variation, the growth rate of sunflowers grown from home-harvested seeds should be comparable to those grown from commercially purchased seeds, provided the seeds are viable and the growing conditions are optimal. Differences may arise due to seed quality, storage conditions, and environmental factors.
Nutritional Needs of Sunflowers
Sunflowers are heavy feeders. They require ample nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium throughout their growth cycle. Nitrogen supports leaf and stem growth, phosphorus promotes root development and flowering, and potassium enhances overall plant health and disease resistance. Soil testing can help determine nutrient levels and guide fertilization strategies.
Yes, you can generally plant sunflower seeds harvested from a mature sunflower head. The success rate depends on factors like seed viability and proper planting techniques. Similarly, you might wonder, can you plant scuppernong seeds , and the answer is also largely dependent on factors like seed quality and growing conditions. Returning to sunflowers, remember to choose plump, healthy seeds for the best chance of germination.
Signs of a Healthy vs. Unhealthy Sunflower
A healthy sunflower displays vibrant green leaves, strong stems, and abundant flowering. An unhealthy sunflower might show signs of wilting, yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or pest or disease infestations. Regular monitoring allows for early detection and intervention.
Harvesting and Seed Collection
Harvesting sunflower seeds at the optimal time and employing proper drying and storage techniques ensures high seed viability for future plantings. Preventing pest damage is also crucial.
Harvesting Sunflower Seeds: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Allow the sunflower heads to fully mature. The back of the head should turn brown and the seeds should be dry and firm.
- Cut the sunflower heads from the stalk, leaving a few inches of stalk attached.
- Place the heads in a dry, well-ventilated area to further dry.
- Once thoroughly dry, rub the seeds from the heads.
- Clean the seeds by removing any debris.
Preventing Pest Damage and Disease
Pest and disease control strategies include crop rotation, using disease-resistant varieties, and monitoring for signs of infestation. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing significant yield losses. Natural pest control methods can be employed, reducing reliance on chemical pesticides.
Drying and Storing Harvested Sunflower Seeds
After harvesting, sunflower seeds should be thoroughly dried to a moisture content of 6-8%. This can be achieved by spreading them in a single layer in a well-ventilated area or using a low-heat dehydrator. Proper storage in airtight containers in a cool, dry place is crucial for maintaining viability.
Optimal Harvest Time for Seed Viability
The best time to harvest sunflower seeds for optimal viability is when the back of the sunflower head turns brown and the seeds are dry and firm. This typically occurs several weeks after flowering. Premature harvesting results in low viability, while delayed harvesting increases the risk of seed damage from pests or environmental factors.
Question Bank
How long do sunflower seeds remain viable?
Sunflower seeds typically remain viable for 1-2 years when stored properly in a cool, dry, dark place.
Can I use any sunflower seeds from the head?
While you can use seeds from anywhere on the head, seeds from the center tend to have higher viability.
What should I do if my sunflower seedlings are leggy?
Leggy seedlings often indicate insufficient light; move them to a sunnier location or supplement with grow lights.
How can I prevent birds from eating my sunflower seeds?
Use netting to protect the developing seed heads from birds.