Can You Plant Seed From Apple?
Apple Seed Biology
Can you plant seed from apple – Understanding the biology of apple seeds is crucial for successful germination and growth. This section delves into the seed’s structure, dormancy mechanisms, nutritional needs, and germination rate variations across different apple varieties.
Apple Seed Structure
An apple seed possesses a hard outer layer, the seed coat (testa), which protects the inner components. Inside, the embryo, the miniature plant, is nestled within the endosperm, a tissue rich in nutrients that sustain the embryo during germination. The embryo itself comprises the radicle (the embryonic root) and the plumule (the embryonic shoot).
Apple Seed Dormancy Mechanisms
Apple seeds often exhibit dormancy, a period of suspended growth. This is primarily due to a combination of factors, including the impermeability of the seed coat, the presence of growth inhibitors, and the need for specific environmental cues to trigger germination. Stratification, a process of cold treatment, is often employed to break dormancy.
Nutritional Requirements for Apple Seed Germination
Successful germination requires a sufficient supply of water, oxygen, and essential nutrients. The endosperm provides initial nutrients, but additional nutrients from the growing medium become crucial as the seedling develops. A well-balanced soil rich in organic matter provides these necessary nutrients.
Germination Rates of Different Apple Varieties
Germination rates can vary significantly among apple varieties. Factors influencing this variation include seed maturity at harvest, dormancy levels, and genetic predisposition. For example, seeds from certain heirloom varieties may exhibit slower germination compared to modern cultivars bred for rapid growth.
Planting Apple Seeds: Methods and Techniques
Successfully planting apple seeds involves careful preparation and execution. This section provides a step-by-step guide for indoor planting, details various seed preparation methods, compares planting mediums, and emphasizes the importance of proper soil drainage.
While growing an apple tree from seed is possible, the resulting fruit might differ significantly from the parent tree. The success rate is also considerably lower compared to using cuttings or grafts. A similar question arises with pumpkin seeds: can you successfully plant them after roasting, as discussed in this article: can you plant roasted pumpkin seeds ?
The answer, much like with apples, depends on various factors, including the extent of the roasting process. Therefore, while both are achievable, success isn’t guaranteed.
Step-by-Step Guide to Planting Apple Seeds Indoors
- Seed Preparation: Clean and stratify seeds (cold treatment for 60-90 days).
- Planting Medium: Use a well-draining seed-starting mix.
- Planting: Sow seeds about 1/4 inch deep in small pots.
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist, but not waterlogged.
- Light: Provide bright, indirect light.
- Temperature: Maintain a temperature around 65-70°F (18-21°C).
Methods for Preparing Apple Seeds Before Planting
Stratification is a crucial pre-planting step. This involves exposing seeds to cold, moist conditions for a period of time, mimicking the natural winter conditions that break dormancy. Methods include storing seeds in a moist medium (e.g., vermiculite) in a refrigerator for several months.
Comparison of Different Planting Mediums for Apple Seeds
| Planting Medium | Drainage | Nutrient Content | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seed-starting mix | Good | Moderate | Easy |
| Vermiculite | Excellent | Low | Easy |
| Perlite | Excellent | Low | Easy |
| Potting soil | Variable | Moderate to High | Easy |
Importance of Proper Soil Drainage for Apple Seed Germination
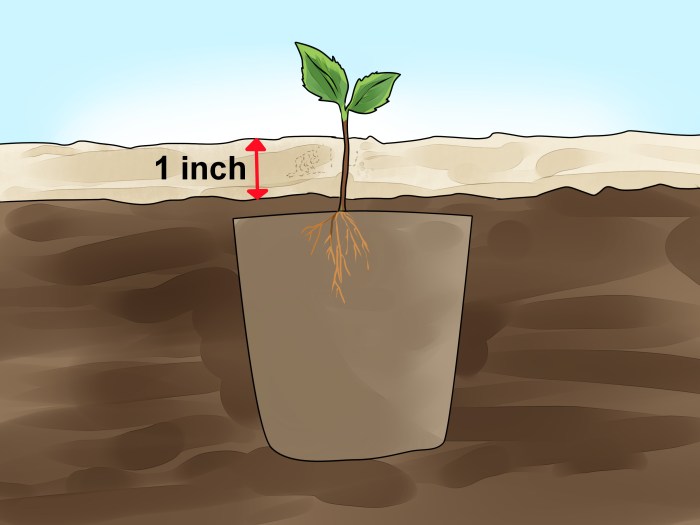
Source: wikihow.com
Good soil drainage is paramount to prevent root rot, a common problem for apple seedlings. Waterlogged soil deprives roots of oxygen, leading to stunted growth or death. Using a well-draining potting mix and ensuring adequate pot drainage are essential.
Environmental Factors Affecting Germination
Several environmental factors significantly influence apple seed germination and seedling growth. This section examines the impact of temperature, light, and moisture.
Impact of Temperature on Apple Seed Germination
Temperature plays a crucial role. Apple seeds generally germinate best within a specific temperature range. Temperatures that are too cold will slow or prevent germination, while excessively high temperatures can damage the seeds.
Optimal Light Conditions for Apple Seedling Growth, Can you plant seed from apple
Apple seedlings require bright, indirect light for healthy growth. Direct sunlight can scorch delicate leaves. Providing adequate light, especially during the initial stages, is vital for strong seedling development.
Role of Moisture in Apple Seed Germination and Seedling Development
Consistent moisture is essential for germination and seedling growth. The soil should be kept moist but not waterlogged. Overwatering can lead to root rot, while underwatering can stunt growth.
Environmental Challenges and Solutions for Growing Apple Seedlings
- Problem: Damping-off (fungal disease) Solution: Use sterile potting mix and ensure good air circulation.
- Problem: Pests (aphids, mites) Solution: Monitor regularly and use appropriate pest control measures.
- Problem: Insufficient light Solution: Supplement with grow lights if necessary.
- Problem: Poor drainage Solution: Use well-draining potting mix and ensure adequate drainage holes in pots.
Apple Seedling Care and Growth
Proper care is essential for the successful development of apple seedlings into healthy young trees. This section Artikels transplanting procedures, pest and disease control, and nutritional requirements.
Steps for Transplanting Apple Seedlings
Once seedlings have developed a few true leaves, they can be transplanted into larger containers or directly into the ground (depending on climate and growing conditions). Handle seedlings carefully to avoid damaging roots.
Protecting Young Apple Seedlings from Pests and Diseases
Regular monitoring for pests and diseases is crucial. Early detection and intervention can prevent significant damage. Organic pest control methods, such as insecticidal soap, are often preferred.
Nutritional Requirements for Young Apple Trees

Source: thespruce.com
Young apple trees require a balanced supply of nutrients for optimal growth. A soil test can determine nutrient deficiencies, allowing for targeted fertilization.
Fertilization Schedule for Apple Seedlings
| Month | Fertilizer Type | Application Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Balanced granular fertilizer | Follow package instructions | Apply after transplanting |
| Summer | Liquid fertilizer | Dilute according to package instructions | Apply every 2-3 weeks |
| Autumn | Balanced granular fertilizer | Follow package instructions | Apply before the first frost |
| Winter | None | – | Tree is dormant |
Challenges and Considerations
Growing apple trees from seed presents several challenges. This section discusses these challenges, the likelihood of genetic variation, and common problems.
Challenges Associated with Growing Apple Trees from Seed
Growing apple trees from seed is more challenging than grafting or purchasing established trees. Germination rates can be low, and the resulting trees may not produce fruit identical to the parent tree.
Likelihood of Genetic Variation in Apple Trees Grown from Seed
Apple trees grown from seed exhibit significant genetic variation. The offspring will not be clones of the parent tree; fruit characteristics (size, flavor, color) may differ substantially.
Common Problems Encountered During Apple Seed Germination and Seedling Growth
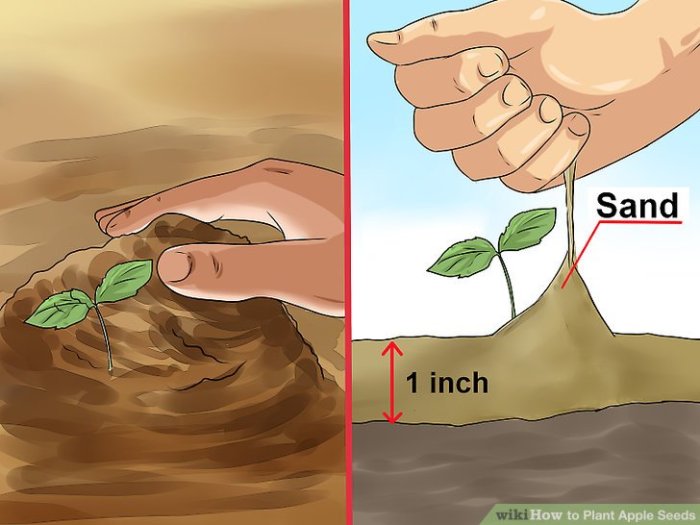
Source: wikihow.com
Common problems include damping-off (a fungal disease), pest infestations (aphids, mites), nutrient deficiencies, and improper watering.
Flowchart Illustrating the Process of Growing an Apple Tree from Seed
A flowchart would visually depict the process, starting with seed collection and ending with a mature tree, highlighting potential failure points at each stage (e.g., seed dormancy, seedling death, pest infestations, etc.).
Visual Representation of Seed Structure: Can You Plant Seed From Apple
The apple seed’s internal structure, as seen in cross-section, reveals a hard, protective seed coat (testa) encasing the embryo and endosperm. The embryo, the miniature plant, consists of a radicle (embryonic root) and a plumule (embryonic shoot). The endosperm, a nutritive tissue, provides sustenance for the developing embryo during germination.
Visual Representation of Germination Process
An image depicting apple seed germination would show the initial swelling of the seed as it absorbs water, followed by the emergence of the radicle (root) pushing down into the soil. Subsequently, the plumule (shoot) would emerge, growing upwards towards the light. This sequence illustrates the transition from a dormant seed to a growing seedling.
Top FAQs
How long does it take for an apple seed to germinate?
Germination can take several weeks to several months, depending on the variety, stratification techniques, and environmental conditions.
Will the apple from the seedling taste the same as the parent apple?
No, the resulting apple will likely be genetically different from the parent apple due to cross-pollination and genetic variation.
What should I do if my apple seedlings develop diseases?
Identify the disease, remove affected parts, and consider using appropriate organic or chemical treatments. Proper spacing and air circulation can help prevent disease.
Can I plant apple seeds directly outdoors?
While possible, it’s generally recommended to start apple seeds indoors for better control over germination conditions and to protect them from harsh weather.





















