Growing Japanese Maples from Seed: Can You Plant Japanese Maple Seeds
Can you plant japanese maple seeds – Cultivating Japanese maples from seed offers a rewarding, albeit challenging, journey for plant enthusiasts. This process requires patience and attention to detail, but the eventual reward of a unique tree grown from seed is significant. This guide Artikels the steps involved, from seed collection to transplanting and ongoing care.
Seed Collection and Preparation
Successful propagation begins with properly collected and prepared seeds. The timing and handling of these seeds are crucial for germination.
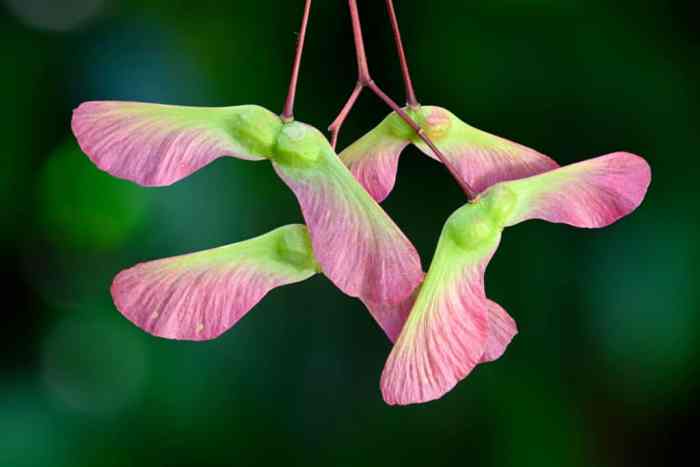
The optimal time to collect Japanese maple seeds is in the late autumn, after the distinctive winged samaras (seeds) have matured and turned brown. They will readily detach from the branches at this stage. Gently collect the samaras, ensuring they are dry and free from damage. Remove the wings from the seeds; these are not needed for germination and can sometimes hinder the process.
Cleaning involves removing any debris or remaining wing fragments.
Seed stratification is essential for successful germination in Japanese maples. This process mimics the natural winter conditions that the seeds would experience in their native environment, breaking dormancy and promoting sprouting. This involves exposing the seeds to cold, moist conditions for a period of time before sowing.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to stratify Japanese maple seeds:
- Mix the seeds with slightly dampened vermiculite or peat moss in a ratio of 1:3 (seeds to medium).
- Place the mixture in a sealed plastic bag or airtight container.
- Store the container in a refrigerator at a temperature between 33°F and 41°F (0°C and 5°C) for 60-90 days.
- Monitor the moisture level periodically, ensuring the medium remains damp but not soggy. Add a small amount of water if needed.
- After the stratification period, remove the seeds from the refrigerator and proceed to sowing.
| Stratification Method | Duration | Temperature (°C) | Success Rate (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refrigerator Stratification (Vermiculite) | 60-90 days | 0-5 | 60-80% |
| Refrigerator Stratification (Peat Moss) | 60-90 days | 0-5 | 60-80% |
| Outdoor Stratification (in a pot, buried) | Winter months | Variable (depending on climate) | 50-70% |
| No Stratification (control group) | N/A | Room temperature | <10% |
Sowing and Germination
The success of germination hinges on providing the optimal environment for the seeds. Proper soil, moisture, and temperature control are crucial factors.
Japanese maple seeds thrive in well-drained, slightly acidic soil (pH 6.0-6.5) rich in organic matter. A seed starting mix is ideal. Sow seeds about ¼ inch deep and spaced approximately 1 inch apart in seed trays or small pots. Maintain consistent moisture by watering gently but regularly, avoiding overwatering which can lead to fungal diseases. High humidity, around 70-80%, promotes germination.
A propagator or covering the seed tray with plastic wrap will help maintain humidity. Ideal germination temperatures range from 65°F to 75°F (18°C to 24°C). To protect seedlings from pests and diseases, use a fungicide or insecticide appropriate for seedlings, following label instructions carefully. Avoid overcrowding to prevent the spread of diseases.
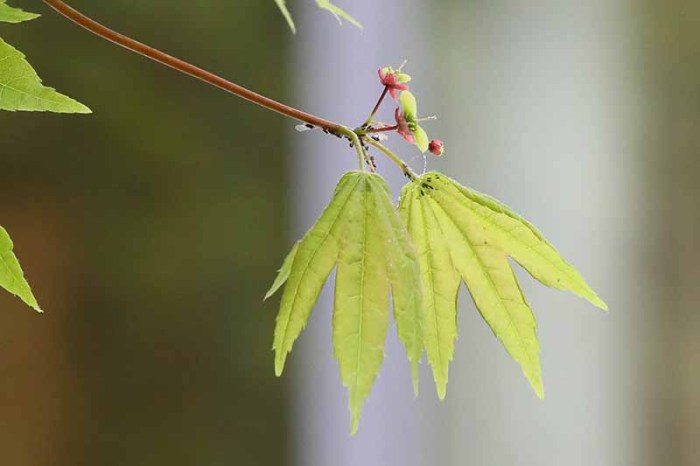
Seedling Care and Transplanting

Source: a-z-animals.com
Recognizing successful germination and providing appropriate care are key to raising healthy seedlings. This section covers crucial steps in seedling development.
Successful germination is indicated by the emergence of a small sprout from the seed. Once seedlings have developed a few sets of true leaves (not the cotyledons), they require regular watering, keeping the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. A balanced liquid fertilizer diluted to half strength can be applied every 2-3 weeks during the growing season. Hardening off gradually acclimates the seedlings to outdoor conditions.
This involves slowly exposing them to increasing amounts of sunlight and wind over a period of 1-2 weeks before transplanting. Transplant seedlings into larger containers or directly into the ground when they are approximately 6-12 inches tall, ideally in early spring or late summer.
- Challenge: Damping-off (fungal disease). Solution: Ensure good air circulation, avoid overwatering, and use a fungicide.
- Challenge: Slugs and snails. Solution: Use slug bait or handpick them.
- Challenge: Slow growth. Solution: Check for nutrient deficiencies, ensure adequate watering and sunlight.
Growing Conditions and Considerations

Source: gardenerspath.com
Understanding the specific needs of Japanese maples is crucial for their long-term health and aesthetic appeal. This includes environmental factors and potential issues.
Japanese maples prefer partial shade to full shade, especially during the hottest part of the day. They thrive in temperatures ranging from 50°F to 80°F (10°C to 27°C). Well-drained soil is essential; poor drainage can lead to root rot. Young Japanese maples require consistent watering, especially during dry periods, but avoid overwatering. Common pests include aphids, spider mites, and scale insects.
Diseases such as leaf spot and verticillium wilt can also occur. Preventative measures include maintaining good air circulation, avoiding overhead watering, and using appropriate pesticides or fungicides when necessary.
| Feature | Growing from Seed | Purchasing Saplings |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Time to Maturity | Several years | Immediate gratification |
| Genetic Variation | High variability | Consistent characteristics |
| Difficulty | More challenging | Easier |
Alternative Propagation Methods, Can you plant japanese maple seeds
While seed propagation offers a unique experience, other methods exist, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Growing Japanese maples from cuttings is another propagation method. Take semi-hardwood cuttings in late summer or early autumn. Dip the cuttings in rooting hormone and plant them in a moist, well-draining medium. Maintain high humidity and warmth. Grafting is another method that allows for the propagation of specific cultivars.
It involves joining a scion (cutting) from a desired cultivar onto a rootstock. This technique requires skill and practice. Seed propagation offers genetic diversity but takes longer to mature. Cuttings are faster but less diverse. Grafting allows precise cultivar reproduction but requires expertise.
- Seed Propagation: High genetic variation, lengthy process, low initial cost.
- Cuttings: Faster growth, less genetic variation, moderate difficulty.
- Grafting: Precise cultivar replication, high skill required, higher cost.
Healthy seedlings display vibrant green foliage, strong stems, and vigorous growth. Unhealthy seedlings may exhibit stunted growth, yellowing leaves, or signs of disease or pest infestation.
Helpful Answers
How long does it take for Japanese maple seeds to germinate?
Germination time varies, but generally, it can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on the stratification method and environmental conditions.
What is the best type of soil for growing Japanese maple seedlings?
Well-draining, slightly acidic soil rich in organic matter is ideal. Avoid heavy clay soils.
Can I use store-bought potting mix for Japanese maple seedlings?
Yes, a high-quality seed-starting mix or a well-draining potting mix is suitable. Ensure it’s not overly compacted.
How often should I water Japanese maple seedlings?
Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Adjust watering frequency based on the weather and soil conditions.
What are the signs of a healthy Japanese maple seedling?
Successfully germinating Japanese maple seeds requires patience and the right conditions. The process is similar in some ways to starting herbs from seed, as discussed in this helpful guide on whether can you plant herb seeds outside , which highlights the importance of soil and sunlight. Understanding these basic principles will significantly improve your chances of successfully cultivating both Japanese maples and herbs from seed.
Healthy seedlings exhibit vibrant green foliage, strong stems, and consistent growth. Look for signs of disease or pest infestation.