Health Benefits and Drawbacks
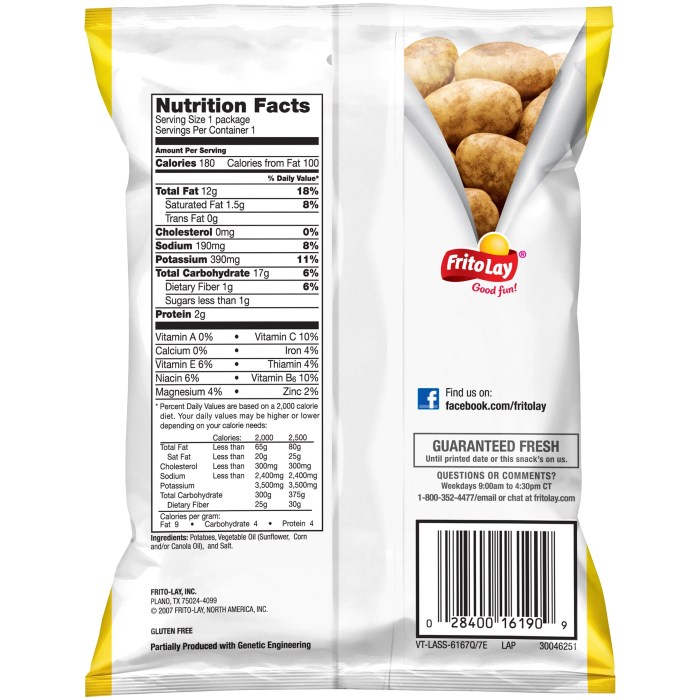

Sweet potato chips nutrition facts – Sweet potato chips, a popular snack, offer a blend of nutritional advantages and potential drawbacks depending on their preparation method and added ingredients. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making informed dietary choices. This section will analyze the health benefits derived from the inherent nutritional profile of sweet potatoes, while also examining potential downsides associated with specific processing techniques and added components often found in commercially available products.
Sweet potatoes are a nutritional powerhouse, offering a significant source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. These nutrients contribute to various aspects of health and well-being. However, the processing of sweet potatoes into chips can alter their nutritional composition, potentially diminishing some benefits or introducing negative aspects. This analysis will explore these contrasting effects.
Nutritional Benefits of Sweet Potato Chips
Sweet potato chips, particularly those prepared through baking, retain a considerable portion of the nutritional value present in the raw sweet potato. They are a good source of Vitamin A (in the form of beta-carotene), Vitamin C, Vitamin B6, and manganese. Furthermore, they provide dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and promotes gut health. The specific vitamin and mineral content can vary depending on factors such as the variety of sweet potato used and the processing method employed.
For instance, baking generally preserves more nutrients than frying.
The fiber content in sweet potato chips contributes to feelings of fullness, potentially aiding in weight management by reducing overall calorie intake. The presence of antioxidants, such as beta-carotene, may also contribute to protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals, thereby reducing the risk of chronic diseases. However, it’s important to note that the overall health impact depends heavily on the preparation method and any added ingredients.
Potential Drawbacks of Sweet Potato Chips
While sweet potato chips offer certain nutritional advantages, several drawbacks warrant consideration. The processing and addition of certain ingredients can significantly impact their overall health profile.
- High Carbohydrate Content: Sweet potatoes are naturally high in carbohydrates. While complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy, excessive consumption can contribute to weight gain if not balanced with adequate physical activity and a controlled overall calorie intake. This is especially relevant for individuals with conditions like diabetes who need to carefully manage their carbohydrate intake.
- Added Sugars and Fats: Many commercially available sweet potato chips contain added sugars and unhealthy fats, such as trans fats, to enhance flavor and texture. These additions significantly reduce the nutritional value and can negatively impact cardiovascular health and contribute to weight gain. Checking the ingredient list is crucial to identify brands with minimal added sugars and fats.
- Acrylamide Formation (Fried Chips): The high-temperature frying process used to produce some sweet potato chips can lead to the formation of acrylamide, a potential carcinogen. This risk is significantly reduced in baked sweet potato chips.
- Sodium Content: Many brands add significant amounts of salt to enhance flavor. Excessive sodium intake is linked to high blood pressure and other cardiovascular problems. Consumers should choose low-sodium options or prepare their own chips to control sodium content.
Baked vs. Fried Sweet Potato Chips: A Nutritional Comparison
The method of preparation significantly impacts the nutritional profile of sweet potato chips. A direct comparison highlights these differences.
| Characteristic | Baked Sweet Potato Chips | Fried Sweet Potato Chips |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Content | Generally lower | Significantly higher |
| Calorie Content | Lower | Higher |
| Acrylamide Levels | Lower | Higher |
| Nutrient Retention | Higher (vitamins, minerals, fiber) | Lower (some nutrient loss due to heat) |
Baked sweet potato chips generally retain a higher proportion of vitamins, minerals, and fiber compared to their fried counterparts. They also contain significantly fewer calories and fat. Fried sweet potato chips, on the other hand, are typically higher in calories, fat, and acrylamide. Therefore, baked sweet potato chips are generally considered the healthier option.
Sweet potato chips offer a tasty, relatively healthy snack, but it’s important to watch your sodium intake. For comparison, you might want to check out the nutritional details of other processed foods, such as spam low sodium nutrition facts , to see how sodium levels vary across different products. Then you can make a more informed choice about how much sodium you’re consuming overall, helping you maintain a balanced diet even with your sweet potato chip cravings.
Ingredients and Processing Methods

The production of sweet potato chips involves a selection of ingredients and processing techniques that significantly influence the final product’s nutritional profile and sensory characteristics. Understanding these factors is crucial for consumers seeking to make informed choices about their snack consumption.Sweet potato chips, at their core, utilize sweet potatoes as the primary ingredient. However, the addition of other ingredients, such as oils, seasonings, and preservatives, can alter the nutritional content considerably.
Processing methods, including frying, baking, and dehydrating, also play a pivotal role in determining the final product’s nutritional value and texture.
Typical Ingredients and Their Nutritional Impact, Sweet potato chips nutrition facts
The following table details common ingredients used in sweet potato chip production and their potential impact on the nutritional value of the finished product.
| Ingredient | Potential Nutritional Impact |
|---|---|
| Sweet Potatoes | Provides carbohydrates, dietary fiber, vitamin A (beta-carotene), vitamin C, and potassium. The nutritional content can vary depending on the variety of sweet potato and growing conditions. |
| Vegetable Oils (e.g., Sunflower, Canola, Coconut) | Adds calories and fat. The type of oil significantly affects the fatty acid profile, influencing the levels of saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fats. Some oils, like coconut oil, are higher in saturated fat than others. |
| Salt | Enhances flavor but contributes to sodium intake, which can be a concern for individuals with hypertension or other health conditions. |
| Sugar | Adds sweetness and can increase the caloric content. Some brands may use added sugars to enhance the flavor profile. |
| Spices and Seasonings (e.g., Paprika, Garlic Powder, Onion Powder) | Contribute to flavor and can add small amounts of certain vitamins and minerals depending on the specific spice. Generally, the impact on overall nutrition is minimal. |
| Preservatives (e.g., Citric Acid) | Extend shelf life, but their impact on nutrition is generally negligible. However, some individuals may have sensitivities to certain preservatives. |
Common Processing Methods and Their Effects on Nutritional Value
Three primary methods are employed in the production of sweet potato chips: frying, baking, and dehydrating. Each method differently impacts the nutritional profile of the final product.Frying, while resulting in a crispy texture, often leads to a higher calorie and fat content due to oil absorption. Baking generally results in a lower fat and calorie content compared to frying, while retaining some of the sweet potato’s nutritional value.
Dehydration, often used to create a healthier alternative, removes water content, concentrating the nutrients but can also potentially lead to a loss of some heat-sensitive vitamins.
Impact of Different Cooking Oils on Nutritional Profile
The choice of cooking oil significantly influences the nutritional profile of fried sweet potato chips. Oils high in saturated fats, such as coconut oil, increase the saturated fat content of the chips, potentially impacting cholesterol levels. Conversely, oils rich in unsaturated fats, such as olive oil or avocado oil, offer a more favorable fatty acid profile, providing potential health benefits associated with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
The smoke point of the oil is also a crucial consideration, as exceeding the smoke point can generate harmful compounds. For example, frying sweet potato chips in olive oil (with a lower smoke point) at high temperatures can lead to the formation of harmful compounds, unlike using a high-smoke-point oil like sunflower oil.
Quick FAQs: Sweet Potato Chips Nutrition Facts
Are sweet potato chips gluten-free?
Usually, yes! But always check the label to make sure there are no added ingredients containing gluten.
Can I eat sweet potato chips if I’m diabetic?
Portion control is crucial. Because of their carb content, diabetics should consume them in moderation and monitor their blood sugar levels.
Are organic sweet potato chips significantly better?
Potentially, they might have slightly higher nutrient content and fewer pesticides, but the difference isn’t always huge. It depends on the brand and farming practices.
How can I make my own sweet potato chips at home?
Super easy! Slice sweet potatoes thinly, toss with oil and seasonings, then bake until crispy. Lots of recipes online!